Message Transmission Process
Objective To enable secure data transmission from senders to receivers via a central server using CipherMQ, leveraging mTLS for authentication and x25519 encryption for message security.
Process Steps
- Initial Setup
- Server Configuration: The server is configured with TLS 1.3 for secure communication.
- Client Configuration: Receivers register their public keys with the server; senders retrieve and load the public keys of intended recipients.
- Message Generation & Encryption
- Senders generate messages in a standardized format: { “message_id”: “”, “sender_id”: “”, “sent_timestamp”: “”, “content”: “” }
- Messages are encrypted for each recipient using their x25519 public key, including message_id, receiver_client_id, and ciphertext.
- Transmission to Central Server
- Senders connect to the server via mTLS for secure authentication.
- Encrypted messages are sent with a publish command.
- The server stores metadata in the table and sends an ACK to the sender.
- Processing & Distribution
- The server queues messages using a high-performance DashMap.
- Based on routing_key and bindings, messages are directed to recipient queues.
- Messages are delivered to connected recipients.
- Reception & Decryption
- Receivers connect to their designated queue, consume messages, and decrypt them using their private key.
- Decrypted messages are saved in a standardized file.
Receivers send an ACK to the server, which updates acknowledged_time in the database, removes the message from the queue, and retains only metadata.
ExampleScenario: Labs and Research Centers
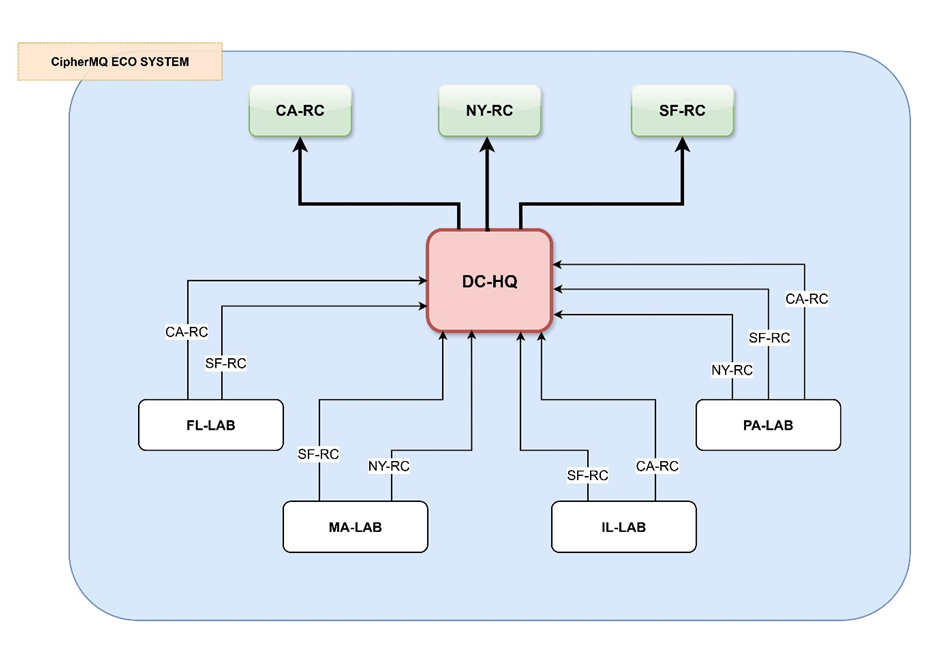
Locations Defined
- Labs (Senders): These generate and encrypt data.
FL-LAB (Florida Laboratory)
PA-LAB (Pennsylvania Laboratory)
MA-LAB (Massachusetts Laboratory)
IL-LAB (Illinois Laboratory)
- Research Centers (Receivers): These receive and decrypt data.
CA-RC (California Research Center)
NY-RC (New York Research Center)
SF-RC (San Francisco Research Center)
- Central Server (Headquarters): server, responsible for managing and distributing messages.
DC-HQ (Washington D.C Headquarters)
Event
FL-LAB: Generates raw data (FL-LAB_DAT_20251008_001), encrypts it for CA-RC and SF-RC, and sends via mTLS to DC-HQ.
PA-LAB: Generates report (PA-LAB_RPT_20251008_125), encrypts it for CA-RC, NY-RC and SF-RC, and sends via mTLS to DC-HQ.
MA-LAB: Generates raw data (MA-LAB_DAT_20251008_045), encrypts it for NY-RC and SF-RC, and sends via mTLS to DC-HQ.
IL-LAB: Generates report (IL-LAB_RPT_20251008_175), encrypts it for CA-RC and SF-RC, and sends via mTLS to DC-HQ.
Processing at Headquarters:
Routes messages to queues (ca_rc_queue, ny_rc_queue, sf_rc_queue) based on routing_key.
Reception at Research Centers:
CA-RC: Receives and decrypts messages from FL-LAB, PA-LAB, IL-LAB.
NY-RC: Receives and decrypts messages from PA-LAB, MA-LAB.
SF-RC: Receives and decrypts messages from FL-LAB, PA-LAB, MA-LAB, IL-LAB.